POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON DYSFUNCTION |
POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON DYSFUNCTION |
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD), also known as adult-acquired flatfoot deformity, is a progressive condition affecting the posterior tibial tendon, which supports the arch of the foot. When this tendon becomes inflamed, overstretched, or torn, it can lead to a collapse of the arch, causing pain, instability, and difficulty walking. PTTD most commonly affects middle-aged individuals and can significantly impair mobility if left untreated.
POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON DYSFUNCTION
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is a condition that occurs when the posterior tibial tendon, which runs along the inside of the ankle and foot, becomes damaged or weakened. This can lead to instability in the foot and ankle and can eventually lead to deformity if left untreated. There are several stages of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, which are determined by the severity of the condition and the level of damage to the tendon.
In the early stages of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, patients may experience pain and swelling along the inside of the ankle and foot. This is often accompanied by a feeling of instability when standing or walking. At this stage, treatment may include rest, ice, and physical therapy to stretch and strengthen the tendon and supporting muscles.
If left untreated, the condition can progress to the intermediate stage. At this point, the pain and instability may become more severe, and patients may begin to notice changes in the shape of their foot. The arch of the foot may begin to flatten, and the heel may start to turn inward, a condition known as "pronation." Treatment at this stage may include the use of orthotic inserts or braces to help support the foot and prevent further deformity.
In the advanced stages of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, the foot and ankle may become severely deformed. The arch of the foot may become flat and the heel may turn inward significantly. Walking may become difficult and painful. At this point, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged tendon and restore stability to the foot and ankle. Following surgery, a lengthy rehabilitation process is typically required to regain strength and mobility.
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is a progressive condition that can lead to significant deformity and disability if left untreated. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing the condition from worsening. If you are experiencing pain and instability in your foot and ankle, it is important to seek medical attention from a qualified healthcare provider.
STAGES OF PTTD
Staging often requires a combination of physical examination and imaging modalities (X-ray or MRI).
🔵 STAGE I - Stage I (PTTD) includes tendinitis. There is inflammation of the tendon causing pain, discomfort. The tendon has not torn but this stage can still cause significant limitations.
🔵STAGE II - There is a partial or complete tear of the tendon accompanied by a foot deformity. The foot is still flexible.
🔵STAGE III - There is a partial or complete tear of the tendon accompanied by a foot deformity. The foot has developed degenerative and arthritic changes causing positional changes in the structure of the foot.
🔵STAGE IV - There is significant damage to the tendon accompanied by a foot deformity that has also led to degenerative and adaptive changes to the architecture of the ankle.
SYMPTOMS
🔵 Pain:
🔹Along the inside of the ankle or foot, especially behind the medial malleolus.
🔹Worsens with activity, such as walking, running, or standing for long periods.
🔵Swelling:
🔹 Around the inner side of the ankle or foot.
🔵 Flat Foot:
🔹A visibly lowering or flattening of the arch of the foot.
🔵Difficulty with Tiptoeing:
🔹Pain or weakness when trying to stand on the toes of the affected foot.
🔵Outward Rolling of the Ankle:
🔹The ankle shifts outward (valgus alignment), making the foot appear turned outward.
🔵Pain on the Outer Foot:
🔹As the condition progresses, pain may also develop on the lateral side of the foot due to increased stress.
🔵Stiffness:
🔹Reduced flexibility or range of motion in the ankle or hindfoot.
CAUSES & RISK FACTORS
🔵Overuse or Repetitive Strain:
🔹Activities like running, hiking, or standing for prolonged periods can strain the posterior tibial tendon.
🔵Trauma:
🔹Direct injuries, such as a sprain or tear of the posterior tibial tendon.
🔵Degeneration:
🔹Age-related wear and tear can weaken the tendon over time (tendinosis).
🔵 Inflammatory Conditions:
🔹Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or gout that cause inflammation in tendons and joints.
🔵Obesity:
🔹Excess body weight increases stress on the tendon.
🔵Flatfoot or Foot Structure Abnormalities:
🔹Congenital or acquired flatfoot can predispose individuals to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.
🔵High-impact activities
🔹Sports like basketball, soccer, or running.
🔵 Improper Footwear
🔹Lack of arch support or wearing worn-out shoes during physical activities.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTS
🔵 Medical History:
🔹Assess symptoms (pain, swelling, flatfoot) and risk factors (e.g., obesity, diabetes, trauma).
🔵Physical Examination:
🔹Inspect for swelling, flatfoot, or ankle misalignment.
🔹Functional tests:
Single-leg heel raise test (difficulty lifting heel or forming an arch).
Gait analysis for foot pronation or instability.
🔵Imaging Studies:
🔹X-rays: Check foot alignment and rule out bone deformities.
🔹MRI: Detect tendon tears, degeneration, or inflammation.
🔹Ultrasound: Evaluate tendon thickening or fluid.
🔹CT Scan: Assess joint deformity in advanced cases.
🔵Lab Tests (if systemic conditions suspected):
🔹Rheumatoid arthritis or gout markers (e.g., RF, uric acid).
NON SURGICAL TREATMENT (Early and Moderate Stages)
🔵 Rest and Activity Modification:
🔹Avoid activities that aggravate symptoms, like prolonged walking or high-impact sports.
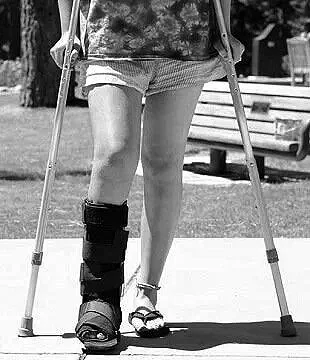
🔵Immobilization:
🔹Use a walking boot or cast to allow the tendon to rest and heal.
🔵Orthotics:
🔹Custom or over-the-counter arch supports to relieve stress on the tendon.
🔹Ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) for added stability in more advanced cases.
🔵 Physical Therapy:
🔹Stretching and Strengthening: Exercises for the posterior tibial tendon and surrounding muscles.
🔹Balance and Gait Training: Correct foot mechanics and strengthen stabilizing muscles.
🔵 Modalities:
🔹Ice, ultrasound, or other therapies to reduce inflammation.
🔵Medications:
🔹Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain and inflammation relief.
🔵Weight Management:
🔹Reduce excess weight to minimize stress on the tendon and foot structure.
MANAGEMENT & TREATMENT
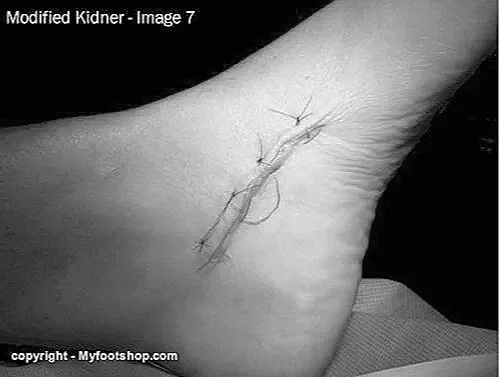
SURGICAL TREATMENT (Advanced Stages or Failure of Conservative Care):
🔵 Soft Tissue Procedures:
🔹Tendon Debridement and Repair: Removal of damaged tissue and repair of the tendon.
🔹Tendon Transfer: Using another tendon (e.g., flexor digitorum longus) to support the damaged posterior tibial tendon.
🔵 Bone Procedures:
🔹Osteotomies: Realignment of foot bones to restore the arch.
🔹Fusion (Arthrodesis): Fusion of affected joints in severe flatfoot deformity.
🔵 Combined Procedures:
🔹A combination of soft tissue and bone surgeries may be needed in advanced cases.
PREVENTION
🔵Wear Supportive Footwear with good arch support or orthotics.
🔵Maintain Healthy Weight to reduce tendon stress.
🔵Strengthen and Stretch the foot and ankle muscles regularly.
🔵Monitor Foot Health for early signs of pain or swelling.
🔵Modify High-Impact Activities and cross-train with low-impact options.
🔵Address Underlying Issues like flat feet or systemic conditions.
🔵Use Braces if needed for support.
🔵Schedule Regular Foot Check-Ups with a specialist.
🔵Avoid Overuse by gradually increasing activity levels and resting as needed.
PROGNOSIS
The prognosis for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD) depends on the stage of the condition and the timing of intervention. Early detection and treatment significantly improve outcomes, while delayed or insufficient care can lead to chronic issues.
🔵Early Stages (Stage I and II):
🔹Good Prognosis: If treated promptly with conservative measures (rest, orthotics, physical therapy, and bracing), symptoms can improve, and further progression may be prevented.
🔹Reversibility: Inflammation and mild tendon damage can heal with appropriate care.
🔵Advanced Stages (Stage III and IV):
🔹Moderate to Poor Prognosis: Structural changes, such as rigid flatfoot or arthritis, are often irreversible.
🔹Functional Limitations: Pain and stiffness may persist, affecting mobility and quality of life.
🔹Surgical Intervention: Reconstruction or joint fusion may be necessary but can improve pain and function when conservative treatment fails.
🔵Factors Influencing Prognosis:
🔹Timely Intervention: Earlier stages respond better to treatment.
🔹Compliance: Adherence to treatment plans (e.g., bracing, physical therapy) improves outcomes.
🔹Patient-Specific Factors: Obesity, diabetes, or systemic conditions can worsen prognosis.
🔵Long-Term Outlook:
🔹With Treatment: Many patients can manage symptoms and maintain mobility, though long-term use of orthotics or braces may be needed.
🔹Without Treatment: Untreated PTTD often progresses, leading to significant pain, deformity, and difficulty walking.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) and preventing its progression. Regularly monitoring your foot and ankle health is especially important if you have risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, or a history of foot injuries. Treatment options range from conservative measures, such as rest, bracing, physical therapy, and custom orthotics, to surgical intervention in more advanced cases. If you notice persistent pain, swelling, or changes in the shape of your foot, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to worsening deformity and long-term complications. Taking proactive steps to maintain healthy foot function can significantly improve your quality of life.